How Does VoIP QoS Improve Calls?
If you’re having issues with call quality when using VoIP, don’t worry, you’re not alone. Many users of hosted phone services face voice quality problems, regardless of their internet connection speed. Fixing sound quality issues in VoIP calls can be difficult, but it’s important to address them as delays and silence can harm your credibility and cost you business opportunities.
Network optimization with Quality of Service (QoS) can solve the problems associated with Voice over IP technology. By prioritizing voice traffic, you can ensure better reliability and clarity of your phone calls. Let us guide you in understanding VoIP QoS, setting it up, and maintaining high call quality with our tips.
What Does VoIP Quality of Service Mean?
VoIP (Voice over IP) technology is vulnerable to network congestion, leading to issues like echoes, delays, and dropped calls. This is because VoIP depends on the timely delivery and proper sequence of data packets. High latency and jitter can significantly affect the quality of VoIP calls.
Quality of Service (QoS) is a solution to this problem. It helps prioritize network traffic, allowing administrators to address audio quality issues. Routers typically handle data packets in a First In First Out (FIFO) order, which can create queuing issues during periods of high bandwidth use. QoS solves this by assigning network resources based on the type of traffic and device.
Setting up QoS for IP telephony may seem unfamiliar, but it will result in improved voice quality without having to sacrifice bandwidth.
Why does Quality of Service matter?
A phone call with bad audio quality feels terrible for everyone participating. No matter the topic, if it’s hard to hear then you’d do anything for the call to drop. Businesses have all kinds of conversations such as:
- Sales demos and webinars
- Customer support
- Employee interviews
- Team meetings with business leaders
Each of these categories are essential. Inconsistent VoIP packets damages brand trust and leads directly to communication failures.
To enhance the call quality for everyone on your Local Area Network (LAN), it’s crucial to understand the workings of VoIP and reduce network congestion by setting up QoS. With the rise of remote work, home networks are facing increased demand from business calls and household data traffic. This highlights the importance of prioritizing VoIP traffic. However, not all VoIP service providers are created equal. Though it may be inexpensive for companies to establish a VoIP system, it doesn’t guarantee reliability. As a result, different VoIP providers offer varying levels of call quality and reliability.
What QoS Does Voice Traffic Require?
To achieve higher call quality than Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) provides, Cisco recommends these standards:
- The default G.729 codec requires packet loss of less than 1% to avoid audible errors. There should be no packet loss for VoIP.
- The ITU G.114 specification recommends less than 150 ms one-way delay for real-time voice traffic.
- Jitter buffers add to the end-to-end delay and are usually only effective on delay variations less than 100 ms. Jitter must be minimized.
Implementing QoS is a must for any VoIP phone service to ensure optimal call quality. Unpredictable events like streaming media and operating system updates can impact the sound of your calls. While QoS may not provide a foolproof solution, it is the best way to optimize your network for better Voice over IP performance. The process of configuring QoS for VoIP is quick and straightforward on most routers, taking only a few minutes.
Best VoIP QoS settings
Common network benchmarks give a framework for getting the phone system in top shape. Knowing these benchmarks helps when troubleshooting VoIP to pinpoint the ideal solution.
- Latency is the time it takes for a data packet to travel from its source to its destination. Every VoIP system and network experiences some degree of latency. However, excessive latency of more than 150 milliseconds in each direction can have a significant impact on voice data packets.
- Jitter (or network jitter) measures the variability in the arrival time of data packets, including latency. In real-time voice communication, network instability can cause packets to arrive in a different order, leading to poor intelligibility in VoIP calls. Significant jitter, exceeding 30 milliseconds, will significantly impact the quality of voice calls.
- Packet loss refers to the amount of data packets that are lost during transmission. The sensitivity of voice data packets to packet loss means that any loss above 3% will result in a noticeable decrease in audio quality.
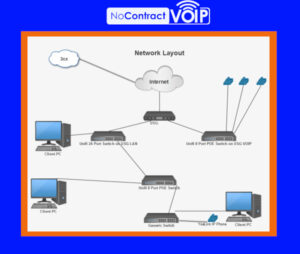
- LAN and WAN network topologies affects your control over its endpoints. A Local Area Network (LAN) refers to the network managed by your router, while a Wide Area Network (WAN) encompasses the larger internet network. VoIP data packets travel from phones through the LAN, and then over the WAN to reach their destination.
Each one of these factors contribute to the overall audio quality of VoIP calls. Setting up VoIP QoS to improve call quality doesn’t take an expert. Most people learn to do it fairly quickly.
Three ways to set up VoIP Quality of Service
It is advisable to familiarize yourself with the documentation provided by the manufacturer of your network equipment, as each router and network setup may differ. Vendor-specific guides on prioritizing voice traffic can often be found in the documentation.
Whenever setting up QoS for VoIP, consider the following approaches:
1) Prioritize Network Traffic By Type, Not Device.
When it comes to allocating network resources, prioritizing traffic by type is the ideal solution. This way, no single device can consume all the available bandwidth. Instead, the priority of traffic is based on its type. If that’s not possible, the next best option is to manage bandwidth for each connected device.
2) Assign Traffic With A DSCP 46 Header As High Priority.
To ensure optimal voice quality on your VoIP calls, it’s recommended to classify network traffic using a DSCP header. The Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP) header allows network switches to prioritize packets based on their priority level. If possible, set up both inbound and outbound RTP packets with DSCP 46.
3) If Supported By Your IT, Set Up Trust Mode With Strict Priority.
By implementing advanced queuing techniques, such as Trust mode and Strict Priority, network switches can prioritize network traffic based on its DSCP headers. This ensures that high priority packets, such as those used in VoIP calls, are given priority over other types of traffic. Most routers offer some form of QoS for VoIP, so even if it’s not as advanced as these techniques, it should still improve the quality of your VoIP calls. If you experience any issues, restart your equipment and contact your business phone service for further testing to determine the cause.
What Improving QoS Settings Can And Can’t Fix
Diagnosing issues with VoIP QoS is possible for most users, but fixing them can be challenging. QoS is just one component of the larger system connecting you to the phone system, and voice packets travel through various network gateways and routers, each affecting call quality. Complex networks with multiple switches and routers may require consultation with a network engineer. QoS won’t impact the performance of your ISP, which governs download and upload speeds, and it won’t affect audio compression, which is determined by VoIP codecs. However, maintaining a stable internet connection is crucial for sound quality. Additional steps, such as prioritizing SIP traffic, disabling SIP ALG, and using VLAN tagging, can further improve VoIP QoS.
Best Practices For Call Quality
For most businesses, the first step in good call quality is to select a reliable business VoIP provider. Trustworthy VoIP providers shed light on their VoIP network and do the work during installation to achieve optimal call quality.
- Use wired Ethernet connections. Wi-Fi is susceptible to interruptions that can negatively affect your phone calls at critical times. A Category 6 Ethernet cable provides low latency and high-speed data transmission, while also eliminating the potential for poor connections.
- Test your LAN and WAN connections often. Monitor your key performance indicators such as latency, network jitter, and available bandwidth to identify network bottlenecks. Keep in mind that VoIP requires a minimum of 100 Kbps of bandwidth per line for both uploading and downloading.
- Count on regularly using 85% of your connection speed, not 100%. Keeping track of key metrics such as ping, jitter, and bandwidth is important in detecting network congestion. VoIP requires an upload and download speed of 100 Kbps per line. For businesses that reach the bandwidth limit of a DSL connection, switching to a cable or fiber connection can provide more bandwidth. Additionally, TCP and UDP connections have overhead that can fully utilize the available bandwidth.
Ready For A Top Notch VoIP Business System?
Want to never have to worry about any of this stuff? We’ll take care of it all for you.
Here at NoContractVoIP, we create custom business phone systems that offer a full suite of hybrid and remote solutions for your telecom needs. Your success is our success.
We don’t try to lock our clients into long term contracts. If you don’t like our services or support, just tell us to cancel and we’ll take care of it. No early termination fees, nobody is stuck for years on end, and we’re motivated to keep our clients thriving.
All of our tech support people live and work near our headquarters in California, and tech support always answers 24/7/365. Our billing and customer support are also based out of the same office, and we guarantee that a live person will always answer our phones.
To get the latest helpful content delivered to your inbox every month, subscribe to our newsletter here.
Looking for the finest stress-free custom business telephone systems? Contact us or call today at 866-550-0005!